How do you know when you have type 2 diabetes? Most of the time you do not have any symptoms or you do not realize you have symptoms. Then you go to your doctor for a physical or another health concern. The doctor orders a blood test and finds you have diabetes. The blood test is called Hgb A1C it shows your average blood sugar level over a 2 to 3 month time period. If your level is 6.5 or greater it indicates you have diabetes. Because you don’t have symptoms you may have diabetes for a while before it is diagnosed.
A small number of people may have symptoms of Diabetes, such as:
- Fatigue
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination (going every 15 to 30 minutes).
- Blurry vision
- increased hunger
- wounds that don’t heal or take a long time to heal
- Unexplained weight loss
- Weight gain

In women, recurring yeast infections and urinary tract infections can also be a symptom of diabetes.
What causes type 2 diabetes?
What causes type 2 diabetes is not completely known however, two things happen. Cells in your body become resistant to insulin. When this happens the glucose in your blood does not enter your cells as it should. The glucose in your blood builds up and this happens repeatedly.
It takes more insulin to get the glucose into the cells where it can be used for energy. The beta cells try to keep up with the demand by releasing more insulin but eventually they are not able to. Glucose/sugar builds up in your bloodstream. You need to take the medication in order to try to keep your blood sugar in a normal range.
Risk factors for getting type 2 diabetes
- A family history of diabetes
- It is more common in people over 40
- It is more common in African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, Asian Americans, and Alaska Natives
LifeStyle Risks
- Poor diet, high carbohydrates, and sugar
- Obesity with fat around your middle
- Stress
- smoking
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Lack of regular exercise
- depression
- prediabetes
- Gestational diabetes and/or having a baby weighing over 9 lbs.
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Fatty Liver Disease
About 80% of people with type 2 diabetes also have fat in their liver according to the Diabetes Institute of Florida. This is called fatty liver disease. The liver stores and releases glucose. This condition makes it harder to control fasting blood sugar. It is caused by obesity. Weight loss can have a positive impact on this disease. In a small number of people, it can turn into permanent liver damage. If you have type 2 diabetes you should ask your doctor if you have fatty liver disease.
Treatment for type 2 diabetes
Treatment, in the beginning, is most often a combination of lifestyle changes and oral medication. Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease and as it progresses you may need to use insulin shots to control it.
Lifestyle changes to treat diabetes include Weight loss, quitting smoking, and exercising daily for at least 30 to 60 minutes. Eat a healthy diet and control portion sizes.
Ask your doctor if you need to monitor your blood sugar levels. If so how often, should you check?
Medications for Type 2 Diabetes
The two most common medications to treat type 2 diabetes are.
Metformin or a generic form of it is usually the first medication that is prescribed. It lowers the amount of glucose released from your liver and helps with insulin resistance. Metformin can be hard on your stomach, often causing gas and diarrhea. Taking the long-acting form of Metformin may help decrease these side effects. The side effects may improve with time also.
Another common type of medication to treat type 2 diabetes is Sulfonylureas. The names these medications go by are glipizide, glyburide, and glimepiride. These medications stimulate your body to release more insulin. One of the side effects of these medications can be low blood sugar. They are usually taken in the morning. So, it is important to eat a breakfast that contains some carbs and protein.

There are many more medications that can be used to treat type 2 diabetes, including insulin. If your doctor prescribes your medication be sure to have them explain how it works. Also, any frequent side effects, and if you need to check your blood sugar.
If your doctor recommends checking your blood sugar. They may say to do fasting blood sugar testing which means in the morning before you eat or drink. To check your blood sugar you will need to have a glucometer kit. The kit usually includes a glucometer, a lancing device, a bottle of test strips, and a logbook to record your test results. Take your blood sugar logbook with you to your doctor’s appointment to show your doctor.
Complications of type 2 diabetes (long term)
Keeping your blood sugars as close to normal as you can help to minimize complications. The common complications are:
1. Diabetic Retinopathy can cause blindness. Diabetics are also at an increased risk of cataracts. Diabetics should have a yearly eye exam.
2. Clogged arteries that cause heart disease, heart attacks, strokes, and impaired blood flow to the kidneys, the legs, and the brain.
3. Kidney disease called diabetic nephropathy
4. Nerve damage called diabetic neuropathy. Causes numbness and tingling in your feet and hands.
5. Poor wound healing. Wounds often occur on the feet.
Check your feet for open areas daily.
Diabetic Complications (short term)
- Hypoglycemia – Low blood sugar can occur especially if you skip meals or exercise more than usual. You are more likely to have low blood sugar if you are on insulin or take sulfonylurea.
Typically a blood sugar below 70mg/dL is considered low. You should have about 4 oz of juice and then eat some carbohydrates with protein. Such as half of a sandwich that contains protein. If your blood sugar drops too low you go unresponsive and need a glucagon shot to treat it.
Signs and Symptoms
- Sweating
- Rapid heartbeat
- Anxiety
- Sleepiness
- Pale skin
- Confusion
- Slurred speech
- Headache
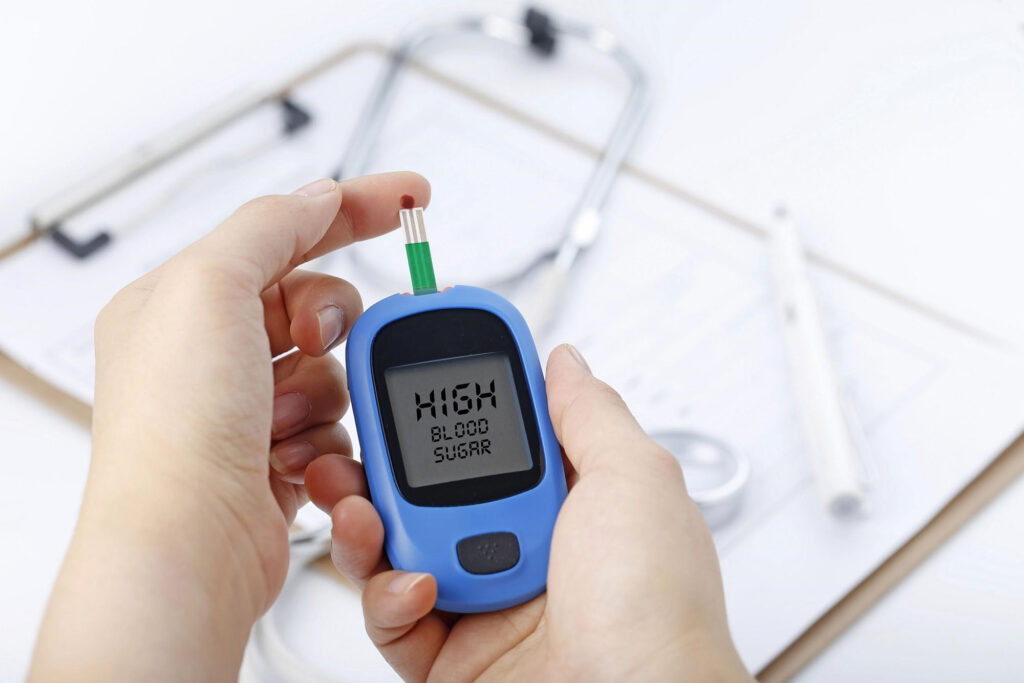
2. Hyperglycemia – High blood sugar level. Is considered fasting (not eating or drinking for 8hrs)
of greater than 130mg/dL. Also considered high blood sugar is a reading over 180mg/dL two hours after a meal. Hyperglycemia is what causes long-term damage to your body, causing long-term complications.
Hyperglycemia usually occurs when you forget to take your diabetes medication. Eat too many carbohydrates. Exercise less than usual. If you have an illness or infection. Treated with higher dose medication, insulin, and exercise.
Signs and symptoms
- Thirst
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Headache
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a disease that can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes. You can significantly improve your type 2 diabetes by losing weight. If you have fatty liver disease it will help that also. Especially if you lose more than 7% of your weight. Try to keep your blood sugars as close as possible to the normal range to decrease long-term complications.

Follow up with your doctor and eye doctor as often as recommended. Know the symptoms of low and high blood sugar. So, you can be prepared to treat them. Check your feet daily for open areas. If you have an open area clean it daily with soap/water and keep it covered. If it is not healing or becomes red, see your doctor. Take care of your health, you only get one body. You can manage your type 2 diabetes, take charge!



